Lab Equipment
Balances : three different balances may be chosen from the Equipment menu or by clicking on the pull-down menu beside the scales button on the toolbar. Any balance may be set to zero by selecting it and using Zero Balance from the Options menu or from the Right-mouse button context menu. Containers with chemicals may be placed on a balance or chemicals may be added directly to it using the Chemicals dialog box. If any items are on a balance when it is zeroed, the balance will show zero mass and readings taken from that point onward will be offset negatively by the mass of these items. These balances enable the user to practice weighing techniques. If all that is required is the mass of a container’s contents, then a weighing scale may be used. This feature displays the mass of the contents below the container and does not require any equipment.
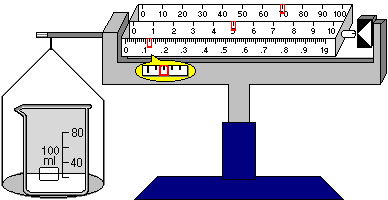
Centigram balance (shown below) has two-decimal place precision and can weigh a maximum of 111g. In this example, the beaker plus contents have a mass of 75.12g. (Note that the yellow balloon is a zoom that displays the indicator for reading the second decimal place.) The pan of the centigram balance may be used to pour or receive the contents of other containers. The centigram balance has three modes: (1) balanced, when the masses on its arm equal the load on the pan and it is ready to read, (2) overweight, when the load is greater than 111g, and (3) underweight, when the balance has been zeroed with a mass on its pan and the mass has been removed.

Electronic balance (shown below) has three-decimal place precision. In this example, the beaker plus contents have a mass of 75.123g. Note that the container will automatically be moved into position.
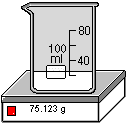
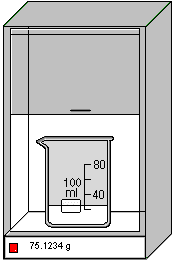
High sensitivity balance (shown below) has four-decimal place precision. In this example, the beaker plus contents have a mass of 75.1234g. Note that the container will automatically be moved into position.
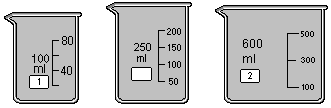
Beaker : wide mouth, thin walled containers with projected lip used widely in laboratory chemistry. ChemLab provides a 100ml, a 250ml and a 600ml beaker. They can be added to the lab space by pressing the toolbar beaker button (100ml), selecting the 100 or 600ml menu items from the equipment menu or right click on the lab space and selecting the beaker menu item from the popup context menu.
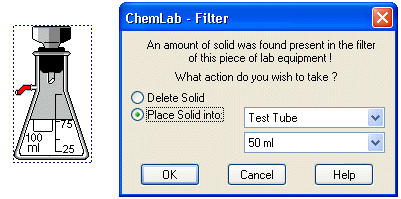
Buchner funnel : a funnel with a flat circular base perforated with small holes used for filtering with suction. In ChemLab a buchner funnel is added either by clicking on the buchner funnel from the toolbar, which adds an erlenmeyer flask with bruchner funnel already inserted, or by first selecting an erlenmeyer flask and then picking the buchner funnel from the toolbar, equipment menu or right-mouse-button context menu. To remove the funnel, select the erlenmeyer flask and pick the buchner funnel from the toolbar, equipment menu or right-mouse-button context menu. If any solid is present in the filter a dialog box will appear asking whether you wish to discard or keep and place it another container.
Bunsen burner : a gas burner used in laboratories. Consists of a metal tube with a valve for controlling the air-fuel mixture. In ChemLab the bunsen burner is added by selecting the bunsen burner button from the tool bar, equipment menu or right-mouse-button context popup menu. If a container is selected when the bunsen burner button or menu item is selected a burner will be added just below the selected container. Lab equipment containers, which allow heating, that are place directly above a bunsen burner, will receive a fixed amount of heating from burner. The amount of heat transfer by a bunsen burner can be varied by changing the burner heat in the Equipment Options dialog box.
Buret : a graduated glass tubes with a stopcock valve used for transferring precisely measured liquid volumes. Used in volumetric analysis in laboratory chemistry. In ChemLab a 10ml and 50ml buret are provided. They can be added to the lab space by pressing the toolbar buret button, selecting the buret from the equipment menu or right click on the lab space and selecting the buret menu item from the popup context menu.
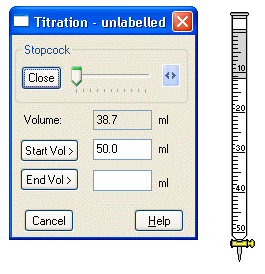
A titration dialog box is opened when a new buret is added. The titration dialog box is used to control the rate of flow leaving the buret. A slider control in the dialog box labeled stopcock is used for this purpose. If an existing buret is selected when the buret button or menu is pressed no new buret will be added, rather the titration dialog box will then refer to the previously selected buret. To identify which buret the titration dialog box refers to, the buret’s label value is added to the dialog box’s menu bar. Note, only one titration dialog box can be opened at a time. The titration dialog box also updates the current volume of the buret to the nearest tenth of a ml and can be used to record the start and end-points of a titration. The Volume displayed is either the Actual Volume or the Scale Volume depending upon the setting in the Equipment Options dialog box. Show Actual Volume is the default setting.
Calorimeter : is an instrument for determining the amount of heat evolved, transferred or absorbed. In ChemLab it consists of a closed insulated vessel with a thermometer. To add a calorimeter to ChemLab select the calorimeter menu option in the Equipment main menu or use right-mouse-context button. The calorimeter has a volume of 250ml and will be open when first added. To close a calorimeter, select it and press the thermometer tool bar button. This will add both a thermometer and a cork top to calorimeter. Doing this a second time will remove the thermometer and open the calorimeter. Note: the calorimeter will only be available for those experiments in which it is used. So the menu option will often appear grayed out.
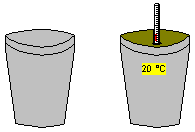
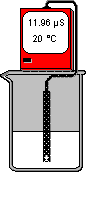
Conductivity Meter : Conductivity is measured by putting a probe in a solution. The meter measures the electrical conductance of the solution between two plates. The instrument reads directly in units of micro siemens (µµS). Temperature of the solution is also displayed in RAW mode. To use the conductivity meter, place it above a beaker , select both objects and combine them.
Temperature has a large effect on conductivity. As the temperature of a solution increases, the conductivity increases. The standard way of expressing the conductivity of a solution is the conductivity at 25 oC . To avoid the necessity of bringing samples to the reference temperature, the conductivity meter can automatically normalise readings to a standard reference by using an Automatic Temperature Compensator sensor ("ATC"). To switch from the RAW conductivity mode to ATC mode, select the meter while it is not combined and use the right-mouse button.
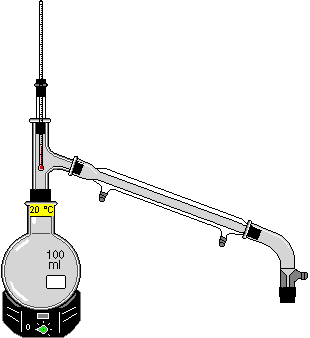
Distillation Equipment : distillation separates the components of a liquid mixture by heating the mixture over the range of its components’ boiling points while simultaneously condensing the vapour. The distillation unit requires assembly. From the Distillation Equipment menu under the ChemLab Equipment menu, first select the Round Bottom Flask (100 ml). Highlight the Round Bottom Flask by clicking on it. From the Equipment menu or from by using a right-mouse click context menu, select the Heating Mantel. Likewise, add the Distillation Head, the Condenser, and finally the Distillation take-off. To add a chemical to the Round Bottom Flask, highlight the whole unit by clicking on it and then call up the Chemicals dialog box by using the context menu or the ChemLab Chemicals menu. The intensity of the Heating Mantel maybe set either from the context menu or the ChemLab Options menu. Note that the Heating Mantel has a red light to indicate that it is turned on and a green dial to indicate the relative heat intensity. To collect distillate, place a graduated cylinder or a beaker under the Distillation take-off spout. The Thermometer units may be set to degrees Celsius, Kelvin or Fahrenheit by selecting Equipment under the ChemLab Options menu.
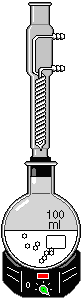
Reflux Condenser : functions like the other distillation equipment insofar as it also separates the components of a liquid mixture by heating the mixture to its boiling point and condensing the vapour. However, the vapour is simultaneously returned to the mixture instead off being distilled off. As a result, the volume of the mixture remains constant while boiling. Using the Reflux Condensor with a Round Bottom Flask requires assembly. The assembly procedure and equipment operation are the same as the regular Distillation Equipment except that the Reflux Condenser is selected in place of the regular Condenser and no Distillation Head is used.
Dumas Bulb : used to determine vapour density according to the Dumas method. In the Dumas method a volatile liquid of unknown molecular weight is placed in the Dumas bulb, which is of known volume and weight. The bulb is placed in a hot water bath and brought to a boil until no liquid remains. The bulb is then weighed to determine the mass of the remaining vapour. Molecular weight can be determined using the ideal gas law.
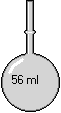
Electrochemical Cell : a half-cell assembly that includes a test tube, two electrodes and a voltage meter. The test tube has a small hole in the bottom. It has been dipped into a hot agar and kNO3 solution in order to form a conductive plug when cooled. The test tube becomes one of the half-cells by filling it with an electrolyte and inserting an electrode. The other half-cell is composed of a beaker also filled with an electrolyte. By placing another electrode along side the test tube and inserting them both into the beaker, a complete cell is formed. The meter applies a voltage that is equal but opposite to the voltage generated by the cell. This reverse potential holds the redox reactions in equilibrium and enables the cell’s output voltage to be measured at a steady-state. All observations taken at STP (25 Celsius and 100 kPa).
Steps to create an electrochemical cell: 1) Select an Electrochemical Cell from the Equipment menu. 2) Choose metals for the Left and Right electrodes from the drop-down lists in the dialog box. (You can verify or change these by selecting the half-cell assembly and re-selecting Electrochemical Cell from the Equipment menu.) 3) Select the half-cell assembly and add at least 4ml of electrolyte to the test tube from the Chemical menu. 4) Obtain a beaker and add enough electrolyte from the Chemical menu to cover one-third of the electrode. 5) Place the half-cell assembly within the beaker by selecting both and combining them. 6) Read the voltage from the meter.
Erlenymeyer Flask : a flat base conical flask with a narrow neck. ChemLab provides a 100ml erlenmeyer flask. They can be added to the lab space by pressing the toolbar erlenmeyer flask button, selecting erlenmeyer flask from the equipment menu or right click on the lab space and selecting the erlenmeyer flask menu item from the popup context menu.
Evaporation Dish : is short wide mouth container with thick walls. ChemLab provides an evaporation dish with a volume of 100ml. They can be added to the lab space by pressing the toolbar evaporation dish button, selecting the evaporation dish from the equipment menu or right click on the lab space and selecting the evaporation dish menu item from the popup context menu.

Eye Dropper : is used to add drops of liquid to a container. The eye dropper is added to the lab space by going to the Equipment menu or using the Right-mouse click . All eye dropper procedures may be selected from either the Procedures menu or using the Right-mouse click. To fill eye dropper, select it and use the add Chemicals or the add Water dialog box. The eye dropper may also be filled with liquid already in a container. Place eye dropper over container, select it and use Extract liquid. It will be placed in the container and will automatically remove itself once it is full. To dispense drops, place eye dropper over container. To start dripping, select Release liquid. If dripping does not occur, raise eye dropper slightly in order to ensure that there is enough clearance between it and the container for drops to appear. To stop dripping, use the Stop liquid/release extraction procedure. Dripping can also be stopped by moving the eye dropper away from overtop of the container and resumed by placing it back over a container. Be careful not to place it over a container by accident when the Release liquid procedure is set. One drop will range in volume from 0.1 ml to 0.2 ml.
Florence flask : is a round container with a long neck and narrow mouth. ChemLab provides an florence flasks with a volume of 100ml. They can be added to the lab space by pressing the toolbar florence flask button, selecting the florence flask from the equipment menu or right click on the lab space and selecting the florence flask menu item from the popup context menu.
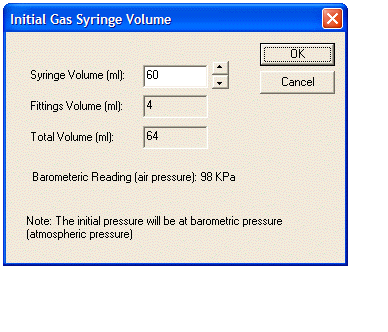
Gas Syringe : is used to investigate the relationship between pressure, volume and temperature. ChemLab provides a Gas Syringe with Gauge (60 ml) to study the relationship between pressure and volume at constant Room Temperature (20 ºC) and a Gas Syringe Sealed (60 ml) to study the relationship between volume and temperature at constant Atmospheric Pressure. When either syringe is selected from the Equipment men, the Initial Gas Syringe Volume dialog box (shown below left) is used to set the initial volume of gas at Atmospheric Pressure and Room Temperature. The syringe volume is recorded by reading the lower level of the plunger within the syringe.
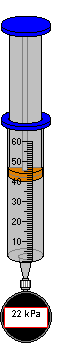
When using the Gas Syringe with Gauge (shown below middle, with gauge) some additional volume may exist in fittings, such as those used to connect the pressure gauge to the syringe. The Total Volume is a combination of the syringe volume and the fitting volume. The pressure is measured at gauge pressure, which is container pressure minus Atmospheric Pressure. The Set Gas Syringe Volume dialog box allows the user to change the syringe volume, which in turn depresses or releases the plunger accordingly. Pressure in kPa is read from the gauge.
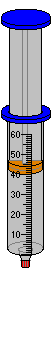
When using the Gas Syringe Sealed (shown below right, without gauge) the Initial Gas Syringe Volume dialog box is also used to set the intitial volume of gas at Atmospheric Pressure and Room Temperature (20 ºC). However, there are no fittings. Therefore, the Fittings Volume is zero and the Total Volume is equal to the Syringe Volume. Since pressure is to remain constant, the syringe volume cannot be changed using the Set Gas Syringe Volume dialog box. To vary the temperature the syringe is heated or cooled by placing it in a hot water or cold-water bath. The corresponding change in volume is read off the syringe. A thermometer can also be attached to display the temperature of the gas within the syringe.
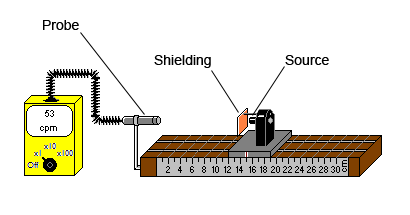
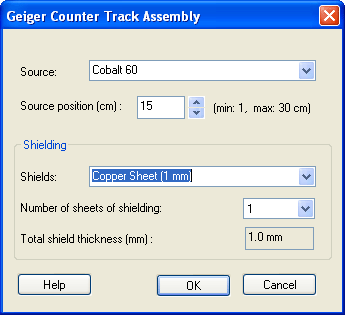
Geiger Counter : is an instrument used to measure radioactivity decay. The instrument’s scale reads counts per minute (cpm). The display will update several times a minute. The Geiger counter track assembly allows the user to select a radioactive source and place it in a precise position from the Geiger counter probe. It also allows the user to select a number of sheets of shielding to absorb the radiation. The source is contained in the source housing. A ruled scale indicates the distance from the Geiger counter probe to the source in centimeters.
When using the Geiger counter you should first determine background radiation and subtract that from the count obtained when measuring the radiation from a source.
Graduated cylinder : is a tall cylindrical container with a finely marked scale, used for precisely measuring out liquid volumes. In ChemLab a 10ml and 100ml graduated cylinder are provided. They can be added to the lab space by pressing the toolbar graduated cylinder button (100ml), selecting the graduated cylinder from the equipment menu or right click on the lab space and selecting the graduated cylinder menu item from the popup context menu.
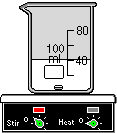
Hot Plate & Magnetic Stirrer : is a piece of equipment used for heating and/or stirring the contents of a beaker or flask. The red lamp on the left indicates that the unit is stirring at the rate indicated on the left-hand dial. The red lamp on the right indicates that the unit is heating at the rate indicated on the right-hand dial.
To use as a hot plate , simply place the container on top of the unit. Note that the container will automatically be moved into position. To regulate the heat, select the unit with a left-mouse click and then call up the context menu with a right-mouse click. From the Hot Plate & Mag Stir Options menu, the heat maybe increased, decreased or turned off. These settings may also be changed by selecting Hot Plate & Heating Mantel under the ChemLab Options menu. The heat transfer rate may be changed using the Equipment Options dialog box. The default is 10 Joules/Sec.
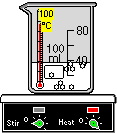
To use as a magnetic stirrer, simply place the container on top of the unit. Note that the container will automatically be moved into position and the stirring stone will appear inside the container. To regulate the rate of stirring, select the unit with a left-mouse click and then call up the context menu with a right-mouse click. From the Hot Plate & Mag Stir Options menu, the stirring maybe increased, decreased or turned off. These settings may also be changed by selecting Magnetic Stirrer under the ChemLab Options menu.
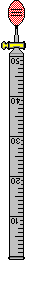
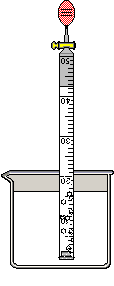
Inverted Gas Buret (50 ml) : is used to measure the volume of gas produced in a reaction at Atmospheric Pressure and Room Temperature. To fill the inverted buret, place it in a beaker by selecting both pieces of equipment and then selecting Combine from under the Arrange menu or from the Right-mouse click. Once the buret is combined with a container, it is filled with the liquid in the container by using the "Fill inverted buret" item from under the Procedure menu or from the Right-mouse click. This will fill the buret to its maximum volume.
Metal Wire : is used in specific labs to hold a small amount of a chemical in place. For example, in the flame experiment, small amounts of water and salt are held under the flame of a bunsen burner until a colour change is observed. (The metal wire is made of nichrome.)
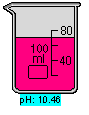
pH Meter : is a display used to measure hydrogen-ion concentration, which is the number of grams of hydrogen ions per litre of an aqueous solution. Since these concentrations are normally very small, the measurement is usually expressed as the logarithm of the reciprocal of the hydrogen-ion concentration of the solution. The result can be used to determine the solution’s acidity or alkalinity. At 25°C, a neutral solution, such as pure water, has a pH of 7; a pH under 7 indicates that the solution is acidic, and a pH over 7 indicates that the solution is alkaline. The pH Meter may be added to a highlighted container by selecting pH Meter from the Equipment menu or using the Right-mouse click context menu. The same procedures may be used to remove the display. This piece of equipment is not available in all lab simulations. The Titration Curve is a related feature that enables the user to collect and plot acid-base titration data. (Note: pH is an abbreviation for potential of Hydrogen.)
Pipet : is used to add and remove liquid to and from a container. The pipet is added to the lab space by going to the Equipment menu or using the Right-mouse click . All pipet procedures may be selected from either the Procedures menu or using the Right-mouse click To fill a pipet, select it and use the add Chemicals or the add Water dialog box. The pipet may also be filled with liquid already in a container. Place pipet over container, select it and use Extract liquid procedure. It will be placed in the container and will extract liquid until it is removed, until the Stop liquid/release extraction procedure is used, or until it is full. To dispense liquid, place pipet over container. To start liquid flowing, select the Release liquid procedure. To stop flowing, select the pipet and use the Stop liquid/release extraction procedure. Flowing can also be stopped by moving the open pipet away from overtop of the container and resumed by placing it back over a container. Be careful not to place it over a container by accident when the Release liquid procedure is set. Shown below are: (a) the pipet in position over a container, (b) the Extract liquid procedure in progress, (c) the Stop liquid/release extraction procedure set or when the pipet is full and (d) the Release liquid procedure in progress.
(a)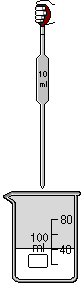 (b)
(b)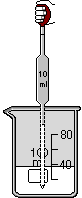 (c)
(c)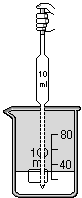 (d)
(d)
Show Weight : in early versions known as “Weighing scale.” It is used for displaying mass only. It will show the sample weight in grams below the container. A weight display may be added to a selected item by pressing the scales button on the toolbar, selecting Show Weight from the Equipment menu or using the Right-mouse click . The weight display is removed from a container by the same process. ChemLab provides balances that may be used to determine the weight of the contents as well as the container. These pieces of equipment enable the user to practice weighing techniques. If Show Weight is activated when there is no lab objected selected or when the selected object cannot be weighed, a centigram balance will be added. In addition, the balances maybe added by clicking on the pull-down menu beside the scales button on the toolbar.
Stirring Rod : is a glass rod used for mixing. ChemLab allows the addition of a stirring rod for mixing to selected lab containers with some contents. The stirring rod may be added to a single selected item by pressing the stirring rod button on the toolbar, selecting stirring rod from the equipment menu or from the popup context menu. A user can also remove an existing stirring rod from a container by this same process. The stirring rod will remain in a container for only a few seconds; to continue stirring the user must re-select the stirring rod. If the container is empty, the stirring rod will appear but will not move until contents are added.
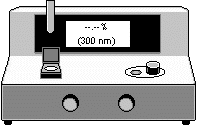
Spectrophotometer : is an instrument that measures the amount of light absorbed by molecules in a solution for a given wavelength. According to the Beer-Bouger Law the quantity of light absorbed by a substance dissolved in a non-absorbing solvent is directly proportional to the concentration of the substance and the path length of the light through the solution.
Beer’s Law is commonly written in the form A=(epsilon)cl, where A is the absorbance, c is the concentration in moles per liter, l is the path length in centimeters, and epsilon is a constant of proportionality known as the molar extinction coefficient. The path length is given to be equal to 1 cm for the spectrophotometer arrangement in ChemLab. The law is accurate only for dilute solutions; deviations from the law occur in concentrated solutions because of interactions between molecules of the solute, the substance dissolved in the solvent.
Percent transmittance (T) and absorbance are terms used to describe spectrophotometric analysis. Percent transmittance is the ratio the amount of light passing through the sample to the amount of light applied to the sample multiplied by 100.
% T = [(light passing through the sample) / (light shined on sample) ]X 100
Absorbance (A) or Optical Density (O.D.) is directly proportional to concentration of solute and it represents the logarithm to the base 10 of the reciprocal of the transmittance.
O.D. can be derived from % T according to the following formula:
O.D. = 2 - log10 of % Transmittance
A Spectrophotometer is added to ChemLab by selecting it from the Equipment menu.
This piece of equipment is not available in all lab simulations. The LabWizard includes an option setting for adding a spectrophotometer to a UDL lab.
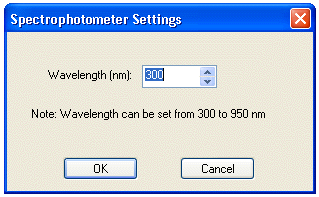
A user can add a spectrophotometer by selecting it from the Equipment menu. A spectrophotometer dialog box will appear that allows the user to specify the wavelength. To change the wavelength on an existing spectrophotometer, first pick the spectrophotometer and again select the "Spectrophotometer…" menu from the Equipment menu or from the Right-mouse context menu . The user should assume that the instrument has already been calibrated and is ready for use at this point.
A fixed cuvette (10ml) is used as a container for the samples. When not inserted in the spectrophotometer, the cuvette will appear above the sample compartment. A sample can be added to the cuvette by selecting the spectrophotometer and using the Chemical dialog box or by pouring into the cuvette from another container.
The display for the spectrophotometer shows the %Transmission (top) and the wavelength (bottom). The %Transmission will be displayed as "--.--%" when the sample is not present in the sample compartment. To insert the cuvette (or sample) pick the spectrophotometer and select "Insert sample" from Spectrophotometer procedures menu (see main procedures menu). To remove a sample, use the "Remove Sample" Spectrophotometer procedure. The Spectrophotometer procedure options are also available from the Right-mouse context menu .
Test Tube : a plain or lipped thin glass tube closed at one end. ChemLab provides an test tube with a volume of 50ml. They can be added to the lab space by pressing the toolbar test tube button, selecting the test tube from the equipment menu or right click on the lab space and selecting the test tube menu item from the popup context menu.

Thermometer : is a instrument for measuring temperature, it consist of a closed narrow graduated tube with a bulb at one end. The tube contains a liquid, such as mercury, whose volume varies with temperature. Temperature is indicated by the height of the mercury column within the thermometer.
ChemLab allows the addition of a thermometer to selected lab containers. The thermometer may be added to a single selected item by pressing the thermometer button on the toolbar, selecting thermometer from the equipment menu or from the popup context menu. A user can also remove an existing thermometer from a container by this same process. The recorded temperature is indicated by the height of the liquid in the tube and additionally by a text field at the top of the thermometer. The scale can be changed from Kelvin, Celsius or Fahrenheit by selecting the temperature scale setting in the equipment options dialog box.
Volumetric Flask: used for preparing dilutions and standard solutions to exacting specifications. A mark on the neck of the flask indicates their precise volume. ChemLab provides 100ml and 250ml sizes. They can be added to the lab space by selecting Volumetric Flasks from under the Equipment menu and then selecting the 100ml or 250ml menu items.
Watch glass : is a short circular glass container, used for measuring out solids and other miscellaneous tasks in the lab. ChemLab provides an watch glass with a volume of 50ml. They can be added to the lab space by pressing the toolbar watch glass button, selecting the watch glass from the equipment menu or right click on the lab space and selecting the watch glass menu item from the popup context menu.